What is it?
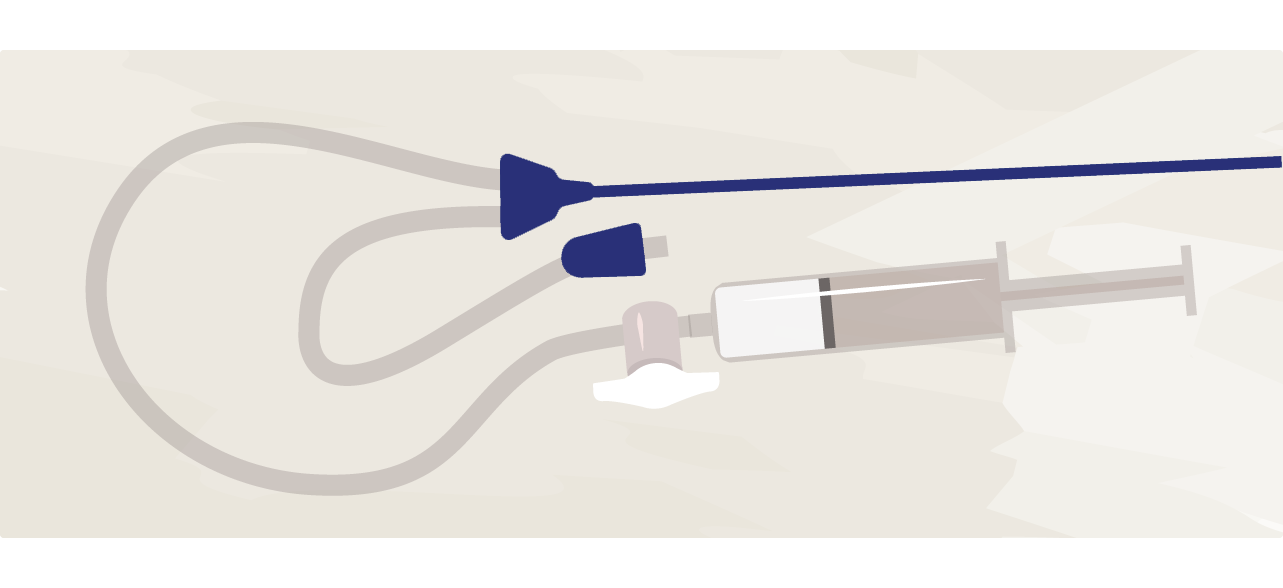
- After sexual intercourse, sperm has to travel from the vagina to the uterus and then to the woman’s fallopian tubes where it could fertilize an egg. The goal of IUI is to insert sperm directly into the woman’s uterus, bringing it as close to the egg as possible. Ovarian stimulation is often added to the procedure to increase the success rate.
Ovarian stimulation
- What is it?
- Ovarian stimulation is used to cause the ovaries to produce more than one egg.
- Medications that can be used for ovarian stimulation:
- Clomiphene citrate
- Letrozole
- Human menopausal gonadotropin (hMG)
- Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
WHAT ARE THE CHANCES OF PREGNANCY PER IUI CYCLE?
- 10-14% when using injectable medications: human menopausal gonadotropin (hMG) or follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH).
- These chances hold for the first 3-4 attempts, after which they decline.
- Chances will be lower if the female partner is older (advanced maternal age is defined as 35 years or older) or if she doesn’t have many eggs left.
- Success rates are also dependent on the cause of infertility.
- Pros:
- Not as invasive or expensive as IVF.
- This treatment has few side effects when used without ovarian stimulation.
- Cons:
- With or without stimulation, there may be discomfort during and/or after the procedure.
- The ovarian stimulation medication can cause:
- Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (swollen and painful ovaries, accumulation of fluid in abdomen and chest).
- Women sometimes report mood swings or feeling overly emotional while taking the hormones needed for stimulation.
- Ovarian stimulation along with IUI carries a greater risk of having a multiple birth. This increases the risk of pregnancy, such as having babies who are born too early and/or low birthweight.